注
分析之间存在依赖关系,某些分析的输入是上步分析的输出,依赖关系会有提示分析过程会有运算量较大的部分,用时较长,请您耐心等待。
此版本最近更新,如遇问题,请随时与我们联系。
单样本分析
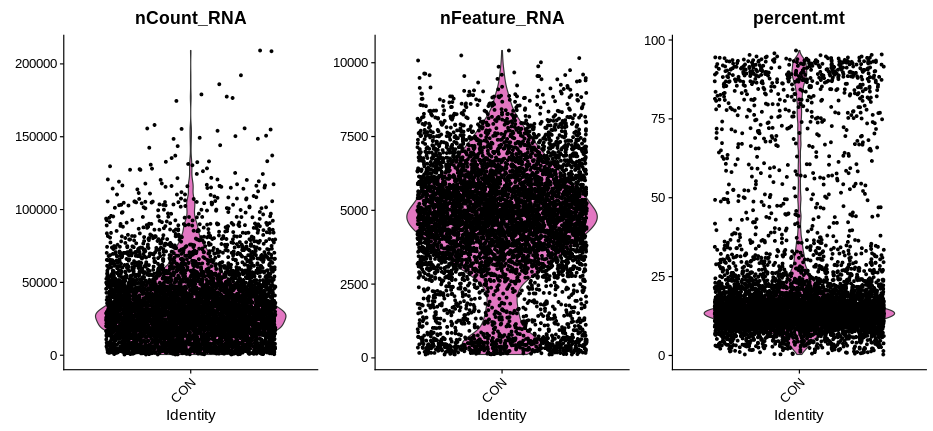
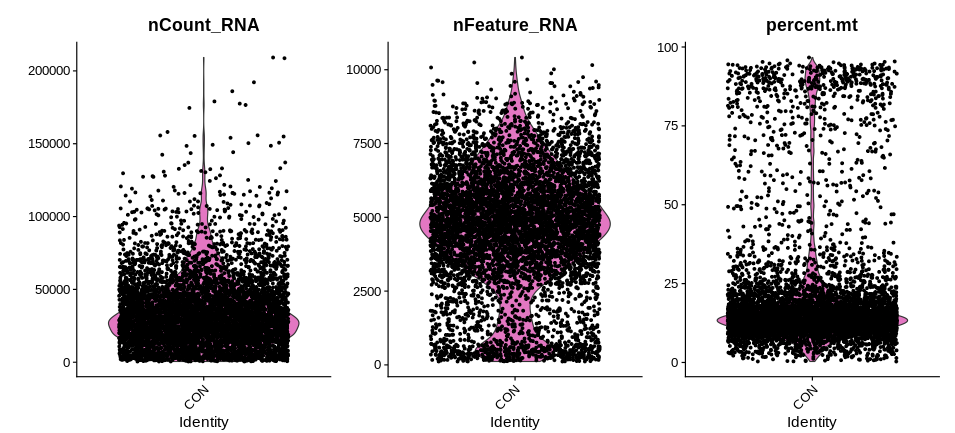
质控与过滤:选择一个样本,通过细胞和基因的过滤指标,对基因和细胞数目进行过滤。原始数据一般为cellranger鉴定的细胞集。
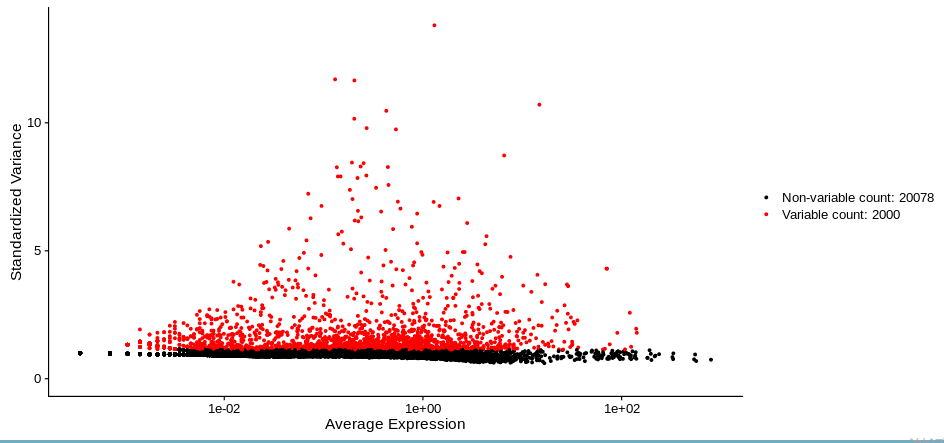
选择高变异基因:对数据进行标准化、中心化,选择高变异基因用于下游分群。
PCA线性降维:通过PCA分析,选取高变异维度用于下游分析。



细胞分群:对细胞进行tSNE或umap分群。

细胞群类型:使用SingleR和已有的数据库鉴定细胞类型。

调整细胞群类型:已鉴定出的细胞群类型,根据差异基因可能有所调整,此功能可以更改鉴定的细胞类群名称。

差异基因:鉴定不同细胞类型间差异基因,可选择“细胞分群”、“细胞群类型”、“调整细胞群类型”这三个功能对应的细胞群名称。

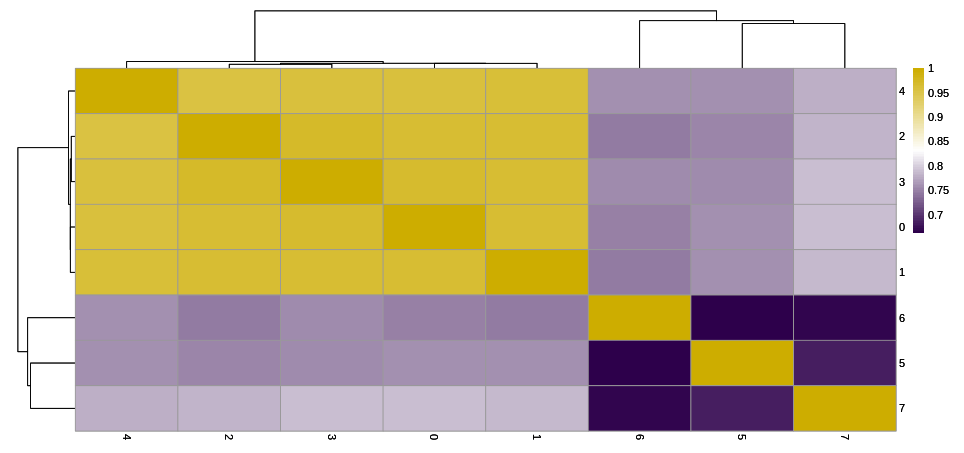
细胞亚群相关性:鉴定“细胞分群”中不同细胞亚群间的相关关系。
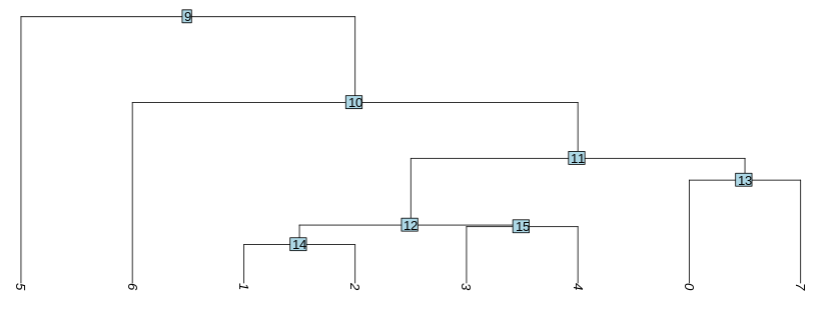
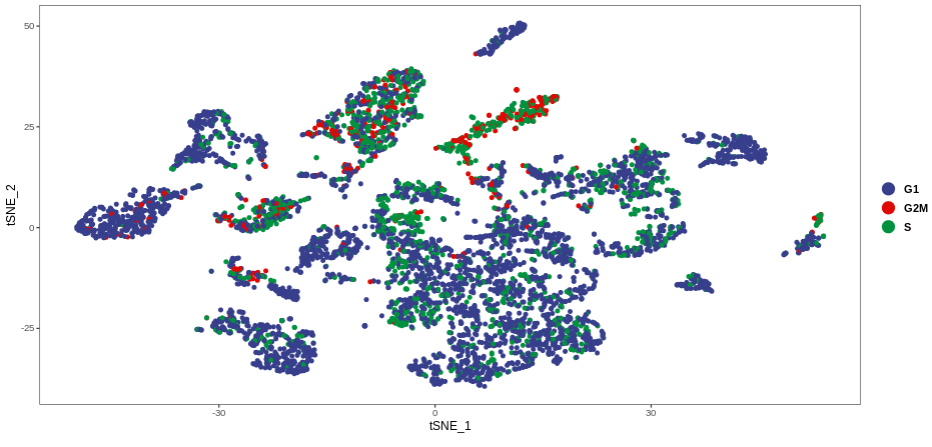
细胞周期分析:根据细胞周期相关基因,对细胞打分,鉴定细胞的周期性。

多样本联合分析
质控与过滤:选择不少于两个样本,通过细胞和基因的过滤指标,对基因和细胞数目进行过滤。原始数据一般为cellranger鉴定的细胞集。
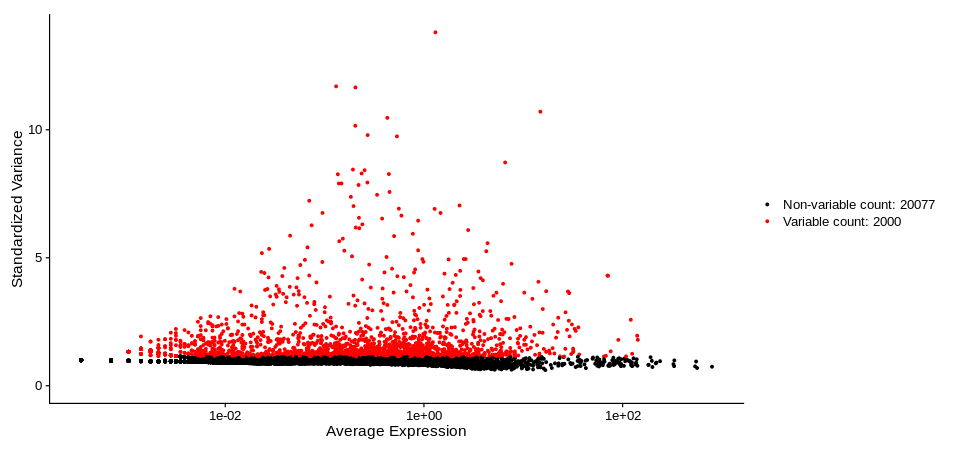
选择高变异基因:对数据进行标准化、中心化,选择高变异基因用于下游分群。
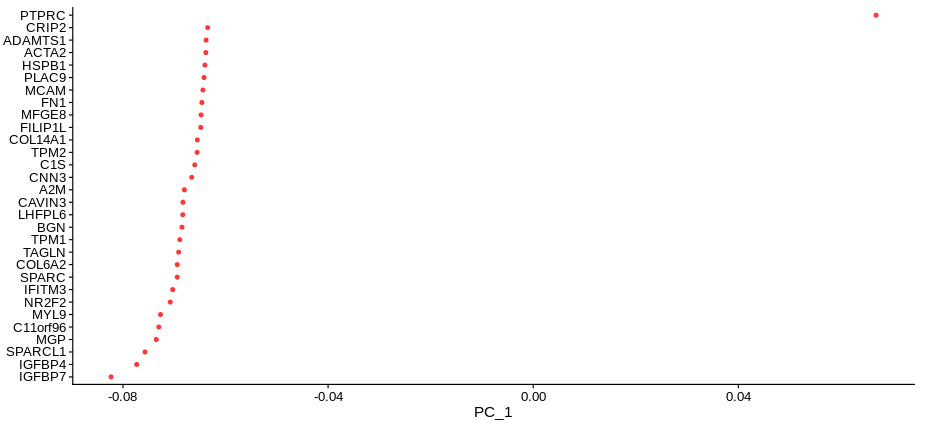
PCA线性降维:通过PCA分析,选取高变异纬度用于下游分析。

细胞分群:对细胞进行tSNE或umap分群。
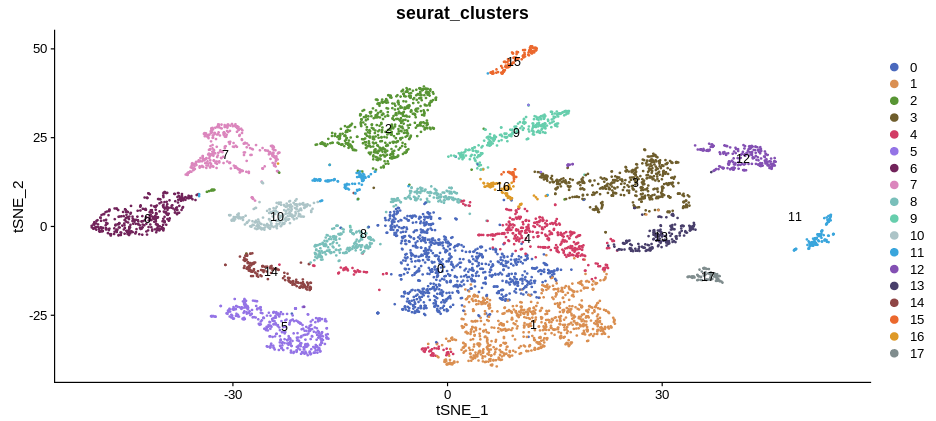
细胞分群:对细胞进行tSNE或umap分群。

细胞群类型:使用SingleR和已有的数据库鉴定细胞类型。
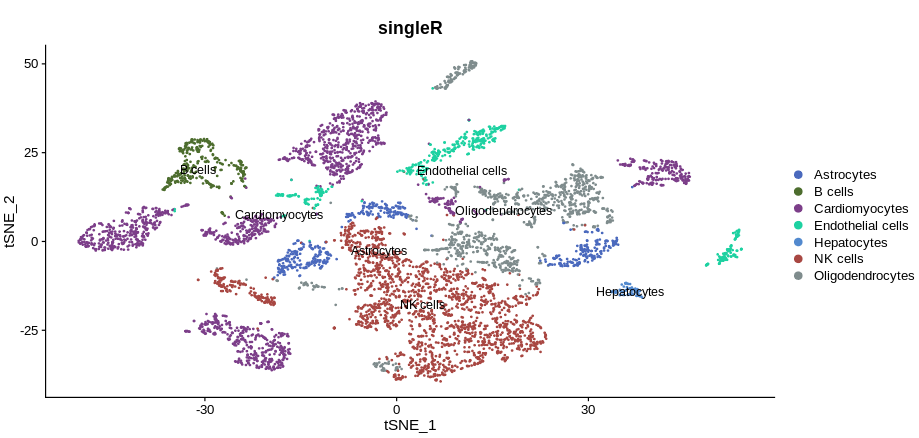
样本间保守的标记基因:样本的不同细胞类群进行差异分群,找出不同样本间共有的差异基因,用于判定细胞类型。
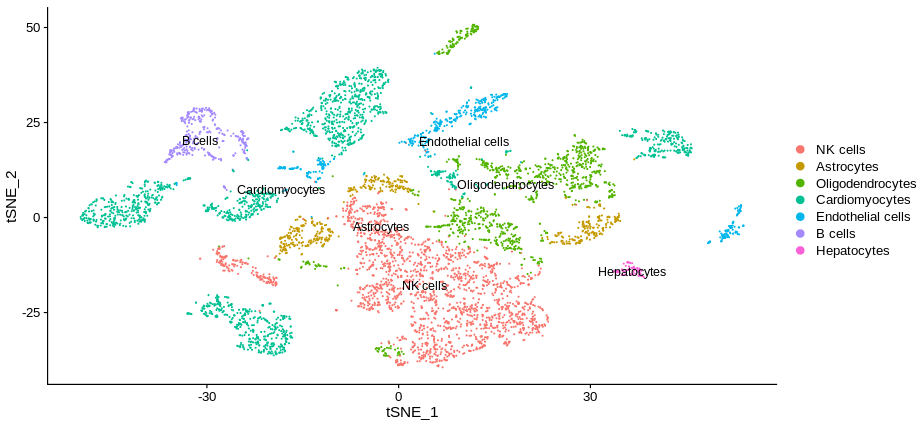
调整细胞群类型:已鉴定出的细胞群类型,根据差异基因可能有所调整,此功能可以更改鉴定的细胞类群名称。
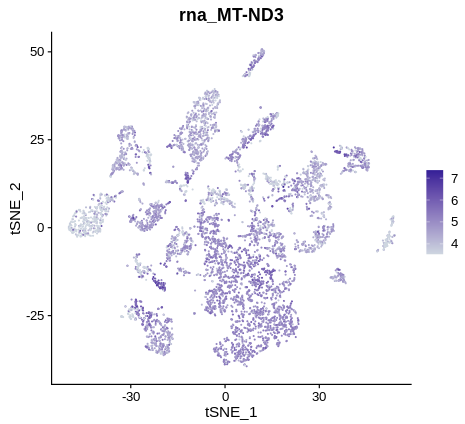
差异基因:鉴定不同样本不同细胞类型间差异基因。
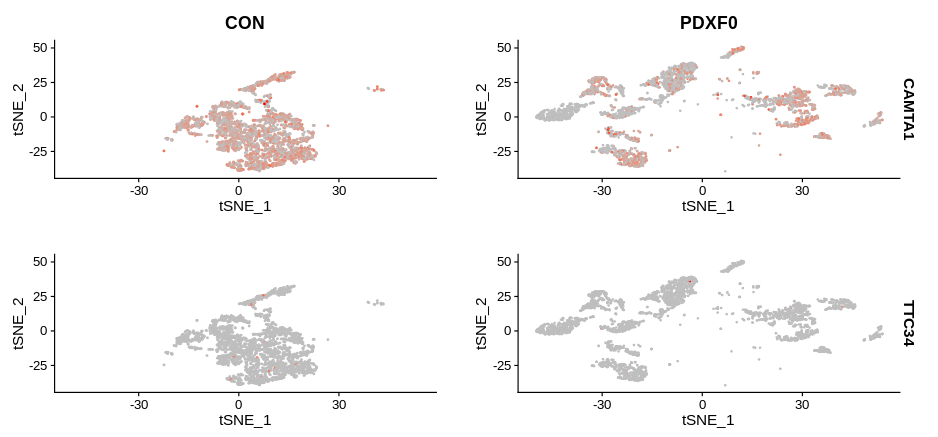
基因表达谱可视化:对基因的表达情况进行可视化。
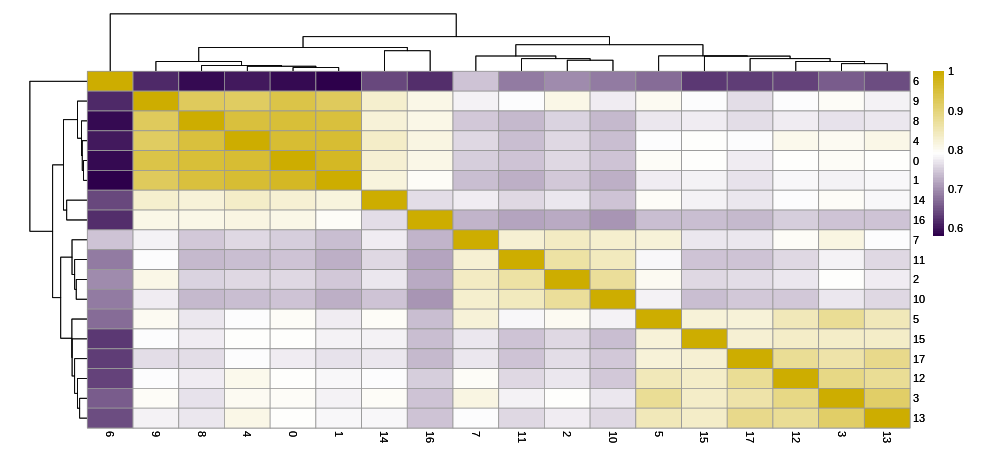
细胞亚群相关性:鉴定“细胞分群”中不同细胞亚群间的相关关系。
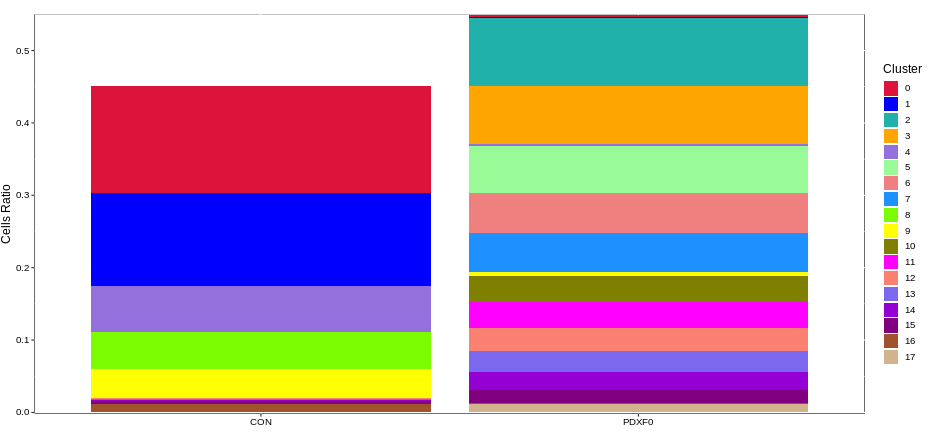

细胞周期分析:根据细胞周期相关基因,对细胞打分,鉴定细胞的周期性。
多样本时序分析
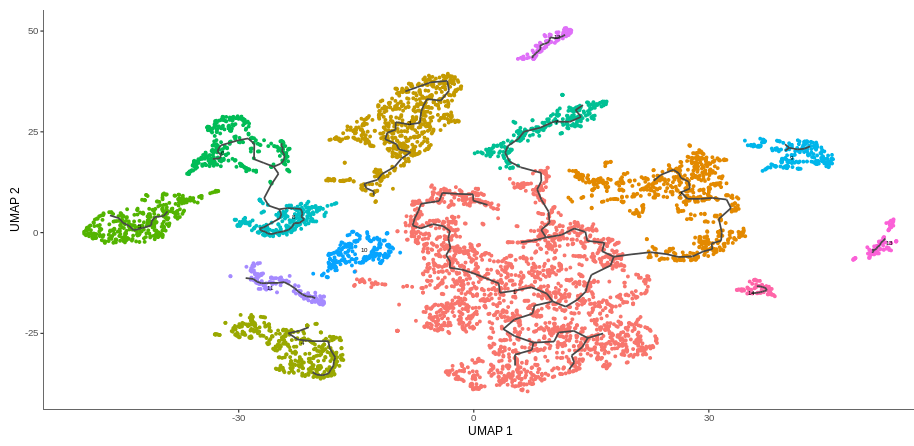
选择数据:选择“单样本分析”或“多样本联合分析”已分群的数据,进行细胞轨迹分群。

时序性分析:根据细胞中基因的表达水平,鉴定细胞时序性性轨迹,并通过自定义的根节点,绘制时序性分布图。

拟时轨迹差异基因:按细胞时序性,计算差异基因,并绘制基因分布图。
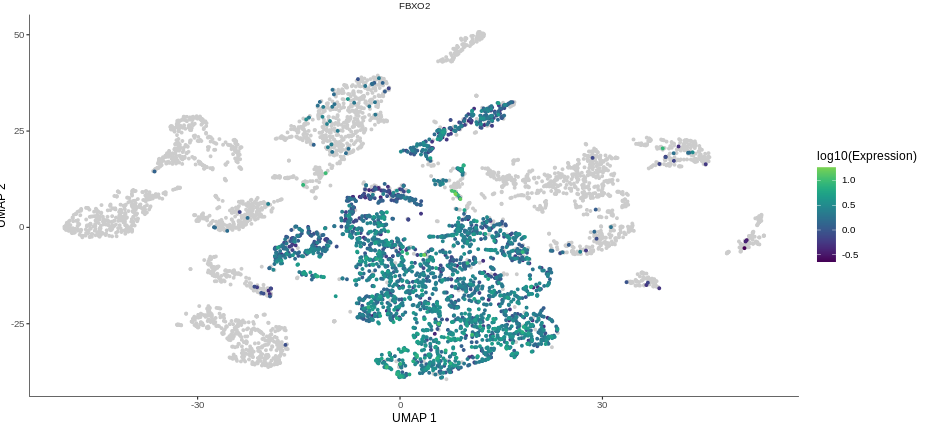
细胞亚群
细胞亚群
细胞类型
基因在样本和群集间的表达
细胞类型定义
各分群内目标基因表达情况比较
细胞群间的差异基因
细胞亚群
细胞亚群
参考文献:
Picelli, Simone et al., Smart-seq2 for sensitive full-length transcriptome profiling in single cells, Nature Publishing Group, 2013.Hashimshony, Tamar et al., CEL-Seq: single-cell RNA-Seq by multiplexed linear amplification, Elsevier, 2012.
Hashimshony, Tamar et al., CEL-Seq2: sensitive highly-multiplexed single-cell RNA-Seq, BioMed Central, 2016.” Bioinformatics 25:765–71.
Macosko, Evan Z et al., Highly parallel genome-wide expression profiling of individual cells using nanoliter droplets, Elsevier, 2015.
Butler, Andrew et al., Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across different conditions, technologies, and species, Nature Publishing Group, 2018.” Bioinformatics 26:139–40.
Trapnell, Cole et al., The dynamics and regulators of cell fate decisions are revealed by pseudotemporal ordering of single cells, Nature Publishing Group, 2014.
Tang, Fuchou, Catalin Barbacioru, Yangzhou Wang, Ellen Nordman, Clarence Lee, Nanlan Xu, Xiaohui Wang, et al. 2009. “mRNA-Seq Whole-Transc riptome Analysis of a Single Cell.” Nat. Methods 6 (5): 377–82.
Picelli, Simone, Åsa K Björklund, Omid R Faridani, Sven Sagasser, Gösta Winberg, and Rickard Sandberg. 2013. “Smart-Seq2 for Sensitive Full-Length Transc riptome Profiling in Single Cells.” Nat. Methods 10 (11): 1096–8.
Hashimshony, Tamar, Florian Wagner, Noa Sher, and Itai Yanai. 2012. “CEL-Seq: Single-Cell RNA-Seq by Multiplexed Linear Amplification.” Cell Rep. 2 (3): 666–73.
Macosko, Evan Z, Anindita Basu, Rahul Satija, James Nemesh, Karthik Shekhar, Melissa Goldman, Itay Tirosh, et al. 2015. “Highly Parallel Genome-Wide ex pression Profiling of Individual Cells Using Nanoliter Droplets.” Cell 161 (5): 1202–14.
Stegle, Oliver, Sarah A Teichmann, and John C Marioni. 2015. “Computational and Analytical Challenges in Single-Cell Transc riptomics.” Nat. Rev. Genet. 16 (3): 133–45.
Jiang, Lichun, Felix Schlesinger, Carrie A Davis, Yu Zhang, Renhua Li, Marc Salit, Thomas R Gingeras, and Brian Oliver. 2011. “Synthetic Spike-in Standards for RNA-seq Experiments.” Genome Res. 21 (9): 1543–51.
Kivioja, Teemu, Anna Vähärautio, Kasper Karlsson, Martin Bonke, Martin Enge, Sten Linnarsson, and Jussi Taipale. 2012. “Counting Absolute Numbers of Molecules Using Unique Molecular Identifiers.” Nat. Methods 9 (1): 72–74.
如果您有什么问题或建议,请与我们联系:bioinfo2@geekgene.com.cn
客服微信:

公司主页:
电话 : 010-62897812 | 官网 : www.geekgene.com.cn | E-mail : service@geekgene.com.cn
QQ : 3323103858 | 地址:北京市海淀区天秀路10号中农大国际创业园1号楼603室
Copyright 2016 All Rights Reserved.北京极客基因科技有限公司 版权所有 京ICP备19041323号
